Clawdbots Explained: Turning AI Agents Into Real workers


In 2026, “How many AI agents work at your company?” is not a thought experiment.
It is a practical question about capacity. About how much work gets done without adding headcount, delays, or handoffs.
Most teams have already discovered the limits of chatbots. They answer questions, then stop. The real opportunity is in AI agents that finish the job.
That is where the Clawdbot comes in. A Clawdbot is an autonomous AI agent built to act. It connects to tools, coordinates workflows, and completes simple tasks from start to finish. Less hand-holding. More momentum.
This guide explains how to run AI agents built with OpenClaw and, more importantly, how to ensure they actually reduce workload and improve response times once they are live.
A Clawdbot (now often referred to as openclaw) is an opensource AI agent platform designed to take ownership of specific pieces of personal work. Instead of assisting a human step by step, it is responsible for moving tasks forward on its own. The focus is execution, not conversation.
The Local Clawdbot with memory idea captures something people have been waiting for. An AI agent that can receive a request, remembers, decide what to do next, and take action without being guided step by step. Not just answering questions, but completing tasks.
This shift signals a broader change. AI is moving from being an assistant that offers suggestions to something closer to a worker that owns parts of a process. That promise is compelling, especially for teams overwhelmed by repetitive requests, manual handoffs, and growing workloads.
What separates a Clawdbot from earlier chatbot tools is how it operates. It is not limited to answering questions or suggesting next steps. It works directly inside your stack, following defined rules and adapting as conditions change.
A Clawdbot typically includes:
The practical benefit is operational. Work that once required several manual handoffs can be completed automatically, response times drop, and teams regain time to focus on higher-impact problems. A Clawdbot shifts AI from being a helper on the sidelines to being an active participant in how the business runs.
To set up OpenClaw (formerly known as Moltbot or Clawdbot), follow these steps to install the core software, configure your AI models, and connect your preferred messaging channel.
1. Installation
The most efficient way to install OpenClaw is via the official curl command on a Linux server or a local terminal (Ubuntu/WSL recommended).
. curl -fsSL https://molt.bot/install.sh | bash.remove the dot, before executing the command.
openclaw onboard2. Configure AI Models
OpenClaw requires an “AI brain” to function. You will need API keys from a provider like Anthropic or OpenAI.
claude-3-5-sonnet or gpt-4o to ensure the bot can handle complex tasks effectively.3. Connect Messaging Channels
Most users interact with OpenClaw via Telegram or Slack for 24/7 access.
openclaw channels login and scan the generated QR code with your phone’s WhatsApp app.You can also use it through the web interface using the command:
openclaw dashboardOpenClaw is designed agents for personal productivity that do real work. Not assistants that answer questions, but systems that observe, decide, and act across tools, environments, and time. The use cases below reflect how OpenClaw agents are already being used in production and experimental workflows.
OpenClaw agents function as a personal execution layer, continuously coordinating data and actions across fragmented tools.
Intelligent Morning Briefings
Agents pull live data from calendars, weather APIs, and news RSS feeds to generate a concise, personalized daily briefing. Delivery happens automatically via WhatsApp or Telegram, with content adapting to location, schedule, and priorities.
Inbox Operations at Scale
Instead of simple classification, agents triage inboxes end to end. They unsubscribe from low-value senders, flag time-sensitive emails, summarize long threads, and draft context-aware replies for human approval. This is particularly effective for operators managing thousands of emails per week.
Natural Language Task Orchestration
Users describe work in plain language and the agent creates, updates, and synchronizes tasks across tools like Notion, Todoist, and Trello. The agent maintains state, resolves conflicts, and keeps task systems consistent without manual intervention.
Automated Expense Capture
Agents convert receipt images into structured financial records. Vendor, date, amount, and category are extracted and written directly into spreadsheets or accounting systems, eliminating manual data entry.
OpenClaw enables agents to operate safely inside engineering environments without exposing raw infrastructure.
CI and Deployment Monitoring
Agents monitor CI/CD pipelines such as GitHub Actions and GitLab CI. Failures, regressions, or successful deployments are surfaced immediately in chat, with relevant logs and next-step suggestions included.
Code Review Intelligence
Agents summarize pull requests, detect risky changes, highlight outdated dependencies, and suggest review comments. This reduces review fatigue and helps teams focus on architecture and correctness instead of scanning diffs.
Controlled Remote Command Execution
Using pre-approved command sets, agents can execute operational tasks like health checks, service restarts, or log inspections directly from chat. This allows safe remote operations without granting unrestricted shell access.
Many high-friction tasks live outside APIs. OpenClaw agents are built to operate in those environments.
Browser-Level Task Execution
Agents can fill forms, navigate websites, scrape structured data, and compile research from sites that offer no APIs. This is commonly used for lead research, pricing analysis, and competitive intelligence.
Smart Home and Device Control
Through Home Assistant integrations, agents trigger devices, manage routines, and coordinate multi-step actions with a single command. Logic and state live in the agent, not in brittle rule chains.
Proactive Monitoring with Heartbeats
Agents periodically check defined conditions such as system status, inbox keywords, or external updates. Users are notified only when action is required, shifting automation from reactive to proactive.
OpenClaw supports agents that plan, negotiate, and operate autonomously across long-running workflows.
Bookings and Negotiation Agents
Agents have been deployed to book restaurant reservations via voice interfaces, research local inventory, and negotiate pricing by emailing vendors or dealerships. These workflows involve planning, tool use, and multi-step decision making.
Agent-to-Agent Networks
OpenClaw agents can connect to environments like Moltbook, where agents interact with other agents, exchange capabilities, and form autonomous communities. This enables experimentation with collective intelligence and distributed task execution.
Most automation tools stop at triggering workflows. OpenClaw enables agents that understand context, maintain state, and take action across systems. These use cases are not edge experiments. They represent the baseline for how software will operate as agents become first-class actors in digital system
If you want, I can also adapt this section for developer docs, a product landing page, or a technical deep dive comparing OpenClaw to traditional automation frameworks.
| Aspect | Clawdbot | YourGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | Personal AI assistant | Business AI agent platform |
| Core use case | Automating individual or personal tasks | Automating Customer support, Sales and business workflows |
| Typical users | Individuals, developers, power users | SaaS, Support and enterprise teams |
| Deployment model | Requires manual setup and deployment | Everything managed for business |
| Task scope | Personal productivity and lightweight automations | Customer support, sales qualification, operations workflows |
| System integrations | Scripts, local tools, personal environments | CRMs, databases, internal tools, SaaS platforms |
| Workflow complexity | Moderate | Multi-step, conditional, enterprise-grade workflows |
| Reliability expectations | Best-effort automation (user-managed) | Deterministic, production-ready execution |
| Governance and auditability | Limited or user-managed | Built-in audit logs, access control, and operational visibility |
| Human handoff | Not a primary design focus | Native escalation to humans with full context |
| Multi-channel support | Typically single interface or environment | Web, messaging platforms, internal tools, and integrations |
| Target outcome | Save time on personal tasks | Reduce operational load and improve response times |
Clawdbot works well as a personal assistant that automates individual tasks and experiments with agent-based workflows. It is flexible and powerful for users who are comfortable deploying and managing their own setup.
YourGPT is designed for a different problem. It focuses on running AI agents inside real business environments, where reliability, governance, integrations, and team workflows matter. Instead of automating tasks for one person, it helps organizations move work end to end across systems and teams.
Seen together, they reflect the same direction. AI agents owning work. The difference is scale, structure, and responsibility.
Creating an AI agent with YourGPT does not start with complex setup or technical decisions. It starts with clarity about what work you want the agent to own. From there, the platform is designed to move quickly without forcing teams into long implementation cycles.
Teams begin by setting up a YourGPT account and deciding what the first agent should handle. This is usually a narrow, high-volume task such as customer support triage, lead qualification, or internal request handling. Starting small makes results visible faster.
Once your account is ready, the next step is teaching your AI about your business.
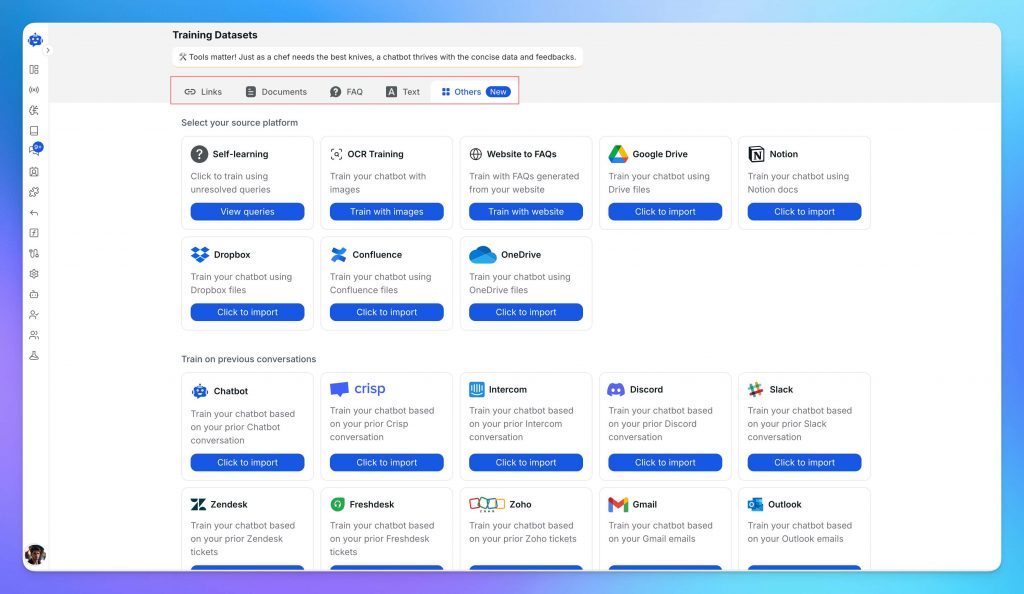
Upload your business content from multiple sources including website pages, documentation, PDFs, knowledge base articles, YouTube videos, multimedia content, and integrations with Notion, Dropbox, Confluence, and many more data sources.
YourGPT learns from your content, understanding your brand, products, and policies automatically.
With your AI trained, you’re ready to configure how it interacts with customers.
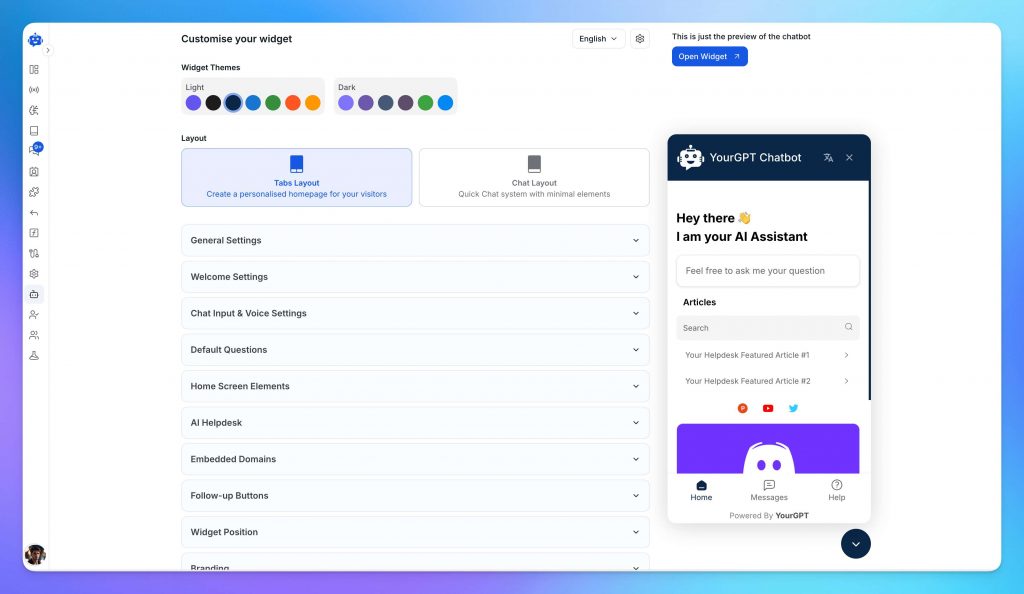
YourGPT gives you complete control over appearance, tone, branding, and domain so your AI agent fits your business perfectly.
For use cases that require high reliability, you can build custom multi-step processes using the AI Studio. This allows you to define business logic, design conditional workflows, and create automations tailored to your specific requirements. Studio provides enterprise-grade control while remaining accessible to teams without deep technical expertise.
Before launching to your customers, it’s important to test everything thoroughly.
Agents are tested in preview mode to simulate real conversations and edge cases. Teams refine responses, verify workflows, and ensure escalation behaves as expected. This step reduces surprises once the agent is exposed to real users.
Launch your AI agent wherever your customers are. Deploy on web and mobile through website widgets, web app embeds, and mobile SDKs. Connect to messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, Telegram, and Slack. Integrate with Shopify, WordPress, Crisp, Zapier, and 100+ tools via MCP. Add browser extensions for Chrome and Firefox.
Enable seamless handoff to human agents when needed for complex queries.
You’re now live with complete AI automation across support, sales, and operations. Your AI will continue learning and improving as it interacts with customers.
As AI agents become easier to deploy, many teams move quickly, often before they have fully defined how the work should be owned and completed. The agents technically function, but the impact falls short. This usually has less to do with the technology itself and more to do with how the agent is designed and introduced into existing workflows.
Teams that avoid these mistakes treat AI agents as part of their operational infrastructure, not as experiments. When agents are designed with clear ownership, boundaries, and accountability, they stop being impressive demos and start delivering consistent, real-world value.
Clawdbot is a personal assistant platform that can automate a set of personal tasks once you deploy and configure it. It is commonly used by individuals and builders who want to run an agent in their own environment and connect it to the tools they use day to day.
When most people talk about Clawdbots, they are often describing a concept or use case for Claude-powered AI bots. In that context, they mean an AI agent that can operate across tools, follow workflows, and act on behalf of a business or an individual.
It depends on what you are trying to do. Clawdbot is well-suited for personal assistant workflows and individual automation where you are comfortable deploying and managing the setup yourself. YourGPT is built for business use, where teams need production workflows, system integrations, governance, and reliable operation across customer support, sales, and operations. Both have advantages, they are designed for different scopes.
A chatbot answers questions and stops. An AI agent is expected to carry a task forward, collect what is needed, follow steps, and complete actions when it can. In practice, users finish work instead of being told what to do next.
In most teams, ownership moves away from engineering quickly. Support, operations, or growth teams manage the agent because they understand the workflows and content best. YourGPT is designed so these teams can update knowledge and workflows without creating technical bottlenecks.
Yes. Many teams train agents on help articles, internal guides, FAQs, and process documentation together. When sources are updated, the agent can be refreshed to keep answers and behavior aligned with current policy.
The agent should stop and escalate rather than improvise. Teams define escalation rules based on missing information, repeated confusion, exceptions, or sensitive topics. When escalation happens, the full context is passed along so users do not need to repeat themselves.
Clawdbot works well as a personal assistant, but business environments often require clearer security boundaries. Because it is open source and self-deployed, teams are responsible for access control, data handling, auditability, and ongoing maintenance. For many businesses, especially those handling customer or internal data, this can introduce additional complexity.
OpenClaw shows what changes when AI agents are designed to carry responsibility instead of offering suggestions. By owning specific tasks, Clawdbots reduce the friction that comes from constant handoffs, reminders, and manual follow-ups. For personal productivity and low-risk workflows, this model works well because it keeps execution moving without demanding ongoing attention.
What matters most is not how advanced the agent is, but how clearly its role is defined. When an agent is given a narrow scope, access to the right tools, and clear escalation rules, it stops being an experiment and starts behaving like part of the workflow. That is where OpenClaw is strongest, enabling individuals and teams to automate real work without heavy process changes.
In organizational settings, the same execution model applies to customer support, sales, and custom workflows, but with additional controls. Work needs to move across teams, systems, and channels with consistency, visibility, and accountability. This is where YourGPT fits naturally. It takes the agent ownership approach and applies it to production environments, handling support requests, sales qualification, and operational workflows while providing the governance and reliability teams need.
Together, they point in the same direction. AI agents are becoming participants in how work gets done. Not by replacing people, but by removing the friction that slows execution. When agents own the routine, humans can focus on the work that actually requires judgment.
Build Clawdbot-style AI agents for your business with YourGPT to handle support, sales, and operational work.
No credit card required • Full access • Limited time offer

Something Fundamental Is Changing About How Work Gets Done For a while, the honest answer to “should we use AI” was genuinely unclear. Some teams tried it and found real value. Others spent months on ai tools that created more overhead than they removed. The technology was real but the fit was uncertain, and uncertainty […]


Nearly 70% of shoppers who add something to their cart leave without buying (glued). Some were never serious. But a lot of them had a question, needed a fast answer, and moved on when one did not come. That is the actual problem AI chatbots solve in DTC, when built correctly. A specific shopper, a […]


Small and medium businesses are facing a structural shift. Customers expect instant responses. Work happens across dozens of tools. Teams remain lean. Costs keep rising. Yet service quality is expected to match large enterprises. For years, businesses depended on chatbots, helpdesks, and manual workflows. These systems offered limited relief, handling basic questions and ticket routing […]


Automation defines how modern enterprises execute, respond, and grow. Customer conversations are handled by AI. Transactions move through automated workflows. Approvals route across departments without manual follow-ups. In high-performing organizations, intelligent systems are embedded directly into revenue operations, service delivery, finance, and internal support. Investment trends confirm this shift. The global conversational AI market surpassed […]


Access to clear, accurate information now sits at the center of customer experience and internal operations. People search first when setting up products, reviewing policies, or resolving issues, making structured knowledge essential for fast, consistent answers. A knowledge base organizes repeatable information such as guides, workflows, documentation, and policies into a searchable system that supports […]


TL;DR Agent mining shifts AI from answering questions to executing real work across systems through controlled, repeatable workflows with verification. By automating repetitive operations with guardrails and observability, agents reduce friction, improve consistency, and let humans focus on decisions and edge cases. For a decade, AI was mostly framed as something that answers. It explains, […]
